Industry 4.0: Practical Steps to Implement Digital Transformation in Manufacturing Industry (Whitepaper)

The manufacturing industry is at a pivotal moment, with the rise of Industry 4.0 offering unprecedented opportunities to transform operations and drive business growth. As advanced technologies like IoT, AI, robotics, and big data become increasingly integrated into manufacturing processes, companies that adopt these innovations stand to gain a significant competitive edge.
This whitepaper on industry 4.0 and digital transformation serves as a comprehensive guide for manufacturing leaders looking to navigate the complexities of digital transformation. Whether you are aiming to enhance operational efficiency, improve product quality, or reduce costs, Industry 4.0 holds the key to unlocking new levels of performance and profitability.
At Vrinsoft a leading digital transformation company in UK, we specialize in helping manufacturers implement tailored Industry 4.0 strategies that align with their unique business goals. We are at the forefront of digital transformation and helped many manufacturing businesses achieve their peak operational functionalities with our efforts. By leveraging our expertise, you can ensure a smooth transition to smart manufacturing, minimize risks, and maximize return on investment.
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, represents the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It encompasses a range of advanced technologies that are blurring the lines between the physical and digital worlds, enabling smarter and more efficient production processes. This revolution is driven by the integration of the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems, advanced data analytics, and artificial intelligence, which collectively transform traditional manufacturing practices into interconnected, intelligent ecosystems.
Industry 4.0 is underpinned by several key concepts and technologies that differentiate it from previous industrial revolutions. These include the convergence of digital and physical systems, real-time data analytics, and the use of artificial intelligence to optimize production. Unlike the earlier revolutions, which focused on mechanization, mass production, and automation, Industry 4.0 emphasizes connectivity, flexibility, and personalized production.
Cyber-Physical Systems: Integration of physical processes with digital networks, enabling real-time monitoring and control.
Internet of Things: Network of interconnected devices that collect and exchange data, facilitating smarter decision-making.
Big Data and Advanced Analytics: Analysis of vast amounts of data to uncover insights, optimize processes, and predict trends.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Use of algorithms and learning systems to enhance automation and decision-making.
Cloud Computing: Utilization of cloud-based platforms to store and process data, enabling scalability and flexibility.
Additive Manufacturing: Advanced 3D printing technologies that allow for customized production and rapid prototyping.
Industry 4.0 is a natural progression from previous industrial revolutions, each of which introduced transformative changes to manufacturing. The first revolution brought about mechanization through water and steam power, the second introduced mass production with electricity, and the third revolution focused on automation using computers and electronics. Industry 4.0 builds upon these advancements by integrating digital technologies with physical processes, leading to more agile, efficient, and customizable manufacturing systems.
The primary objectives of Industry 4.0 are to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and increase flexibility in manufacturing. By adopting these advanced technologies, manufacturers can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, product quality, and time-to-market. Additionally, Industry 4.0 aims to create more sustainable production methods by optimizing resource usage and minimizing waste.
Increased Efficiency: Streamlined operations and reduced downtime through predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring.
Enhanced Product Quality: Continuous quality control and optimization enabled by data-driven insights.
Greater Flexibility: Ability to quickly adapt to changes in demand and customize products to meet specific customer needs.
Cost Reduction: Lower operational costs due to automation, energy efficiency, and optimized resource management.
Sustainability: Reduced environmental impact through efficient use of resources and energy.
It’s crucial for manufacturing businesses to assess their current readiness before implementing digital transformation. This involves a comprehensive evaluation of existing processes, technologies, and organizational culture to determine how well-equipped the business is to adopt new digital tools and methodologies. Understanding where the company stands in terms of digital maturity helps in setting realistic goals and developing a tailored transformation strategy.
Before starting the readiness assessment, it’s important to thoroughly evaluate the current manufacturing processes. This means mapping out all key operations, identifying which processes are manual, semi-automated, or fully automated, and analysing the efficiency of each. Look for bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas where data is underutilized. This evaluation will help you understand the gaps that digital transformation can fill.
One of the first things businesses need to evaluate is the automation across different manufacturing processes. It will help them identify which areas still depend on manual labour and which are already automated. Once you learn about this, you can pinpoint the process that digital transformation can automate and improve to reduce errors. This also brings new opportunities to integrate new and advanced technology to the manufacturing floor to enhance productivity.
Assessing how data is currently collected, processed, and used for decision-making is crucial for fully benefiting from digital transformation. This evaluation should include analysing where the data comes from, how it’s processed, and how it’s used to make decisions. Finding any gaps or inefficiencies in data use can uncover opportunities to use advanced analytics and real-time monitoring tools.
Reviewing your current technology systems and their ability to work with new tools is an important step in the digital transformation process. You need to see if your current hardware and software can work with Industry 4.0 technologies like IoT, cloud computing, and automation systems. Knowing the strengths and weaknesses of your technology infrastructure can help you plan any upgrades or changes you might need to make to support smooth integration and growth.
Identifying slow or redundant processes that could benefit from digital optimization is key to enhancing overall operational efficiency. This involves mapping out existing workflows, analysing the flow of materials and information, and pinpointing areas where delays or bottlenecks occur. By recognizing inefficiencies, you can prioritize digital initiatives that streamline processes, reduce waste, and accelerate production cycles.
Assessing the effectiveness of current quality assurance processes and their potential for improvement through digital tools is essential for maintaining high standards in manufacturing. This evaluation should consider the methods used for monitoring and controlling product quality, the frequency of defects, and the responsiveness of quality control measures. Implementing digital solutions like real-time quality monitoring, predictive analytics, and automated inspection systems can significantly enhance the accuracy and consistency of quality control efforts.
Once the current processes are evaluated, the next step is to identify the strengths and weaknesses within the organization. Understanding these elements is critical for leveraging existing advantages while addressing areas of improvement.
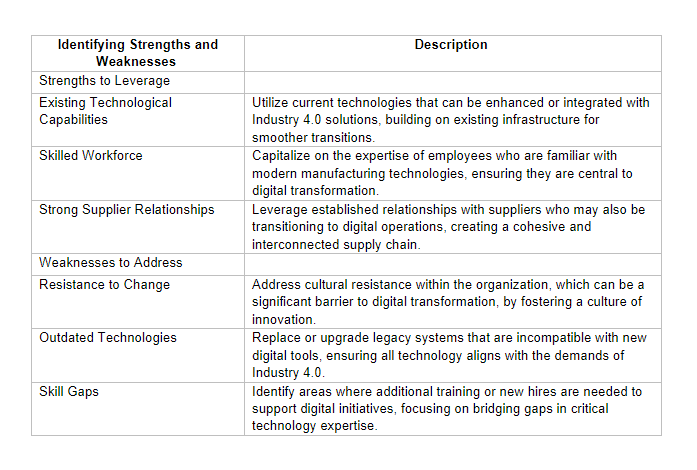
After identifying the strengths and weaknesses, it’s essential to set clear and achievable transformation goals. These goals should align with the overall business strategy and be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Setting the right goals ensures that the digital transformation journey is focused and delivers tangible results.
By carefully evaluating readiness, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and setting clear goals, manufacturing businesses can create a solid foundation for successful digital transformation.
Creating a comprehensive digital transformation strategy is essential for manufacturing businesses aiming to stay competitive in the industry 4.0 era. This strategy should be a well-structured plan that aligns the company’s vision with actionable steps, ensuring that digital initiatives drive meaningful improvements. Here are some of the essential steps that can help your manufacturing business create a digital transformation strategy,
When creating a digital transformation strategy, start by clearly stating the vision and objectives. The vision should describe where the company wants to be in the future, reflecting the long-term goals of the digital transformation. This vision will guide all future actions and decisions, ensuring that every initiative aligns with the overall strategic direction.
Once the vision is clear, specific objectives must be set to make that vision a reality. These objectives should be practical, measurable, and focused on areas that will have the most significant impact on the business.
After defining the vision and objectives, the next step is to create a roadmap that outlines the specific steps and milestones needed to achieve them. This roadmap should detail the sequence of initiatives, allocate resources, and set timelines for each phase of the transformation.
Once you create an effective roadmap for digital transformation for your manufacturing business, the implementation process is straightforward. Here is an example of how we can use various phrases for a successful implementation,
One of the most critical aspects of a digital transformation strategy in the manufacturing industry is ensuring that the chosen technologies align with the specific needs and goals of the business. Technology should not be adopted for its own sake but selected based on how well it can support the company’s objectives, enhance production efficiency, and improve overall operations. In manufacturing, this alignment is key to driving innovation, reducing costs, and maintaining a competitive edge.
Start with a comprehensive assessment of the manufacturing operation’s strategic and operational needs. Identify critical areas such as production efficiency, quality control, supply chain management, and equipment maintenance where technology can provide the most value.
Evaluate various technologies, such as IoT, robotics, AI, and advanced analytics, based on their ability to address the identified needs. Consider factors like scalability to accommodate production growth, integration capabilities with existing manufacturing systems, and overall cost-effectiveness.
Select technologies that can be customized to fit the specific requirements of your manufacturing processes. Ensure that the chosen solutions seamlessly integrate with existing workflows and equipment, enhancing rather than disrupting current operations.
Choose a reliable digital transformation partner who understands the unique demands of the manufacturing industry. Go for partners who not only offer the right technology but also provide strong ongoing support, training, and the ability to scale the solutions as your manufacturing needs evolve.
Consider the future trajectory of your manufacturing business and the industry at large. Select technologies that can evolve alongside your company, supporting innovations such as additive manufacturing, smart factories, and sustainable production practices as they become more prevalent.
Industry 4.0 is powered by a suite of cutting-edge technologies that transform traditional manufacturing processes into smart, interconnected systems. These technologies enable real-time data collection, advanced analytics, and automation, driving efficiency and innovation. By integrating these technologies, manufacturers can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and create more agile and responsive production environments.
Modern manufacturing units can take advantage of IoT technology as it can connect physical devices across the manufacturing floors to communicate and share data in real-time. This connectivity allows for continuous monitoring and optimization of processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced downtime. IoT also facilitates predictive maintenance, helping prevent equipment failures and extending the lifespan of machinery.
Siemens has integrated IoT in their smart factory solutions, using sensors and connected devices to monitor equipment health and predict maintenance needs. This approach reduces downtime and enhances operational efficiency by addressing issues before they become critical.
Manufacturers can use Advanced Data Analytics and Big Data to analyze the large amount of data collected from IoT devices and other sources. This helps companies gain deep insights into their operations, spot trends, and make decisions based on data. These tools improve everything from quality control to supply chain management, making operations more informed and efficient.
General Electric (GE) utilizes big data and advanced analytics through its Predix platform to monitor and optimize industrial operations. The platform processes vast amounts of data from sensors to enhance performance and predict equipment failures across their manufacturing plants.
AI and machine learning are important for smart manufacturing in Industry 4.0. These technologies help systems learn from data, make better decisions, and automate complex tasks. AI-based analytics can predict demand, optimize production schedules, and improve quality control. Meanwhile, machine learning algorithms continuously improve processes for greater efficiency and accuracy.
BMW has implemented AI in its quality control processes. AI-driven image recognition systems help detect defects in components on the production line, significantly improving product quality and reducing waste.
These technologies are central to achieving high levels of precision, speed, and efficiency in manufacturing. Automated robots can perform repetitive tasks with consistent accuracy, reducing human error and freeing up workers for more strategic roles. These systems also enable flexible manufacturing, allowing for rapid reconfiguration of production lines to meet changing demands.
Fanuc uses robotics in its production lines, where automated systems handle repetitive tasks with high precision. This automation not only increases productivity but also allows human workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks.
CPS and Digital Twins bridge the gap between the physical and digital worlds in manufacturing. CPS integrates physical processes with digital control systems, enabling real-time monitoring and optimization. Digital Twins, on the other hand, are virtual replicas of physical assets, allowing manufacturers to simulate and optimize processes before implementing changes, reducing risk and enhancing efficiency.
Rolls-Royce leverages digital twin technology to create virtual models of their jet engines. These digital twins simulate real-world operations, enabling the company to monitor performance, predict maintenance needs, and optimize engine design.
Successfully implementing Industry 4.0 technologies in manufacturing requires a strategic approach that balances innovation with practicality. The following steps outline how manufacturers can effectively integrate IoT and smart devices, leverage data for better decision-making, automated processes, and ensure robust cybersecurity and data privacy. These steps serve as a guide to navigating the complexities of digital transformation while maximizing benefits and minimizing risks.
Integrating IoT and smart devices is the foundation of any Industry 4.0 strategy. To start, manufacturers should identify key areas where IoT can deliver the most value, such as monitoring machine performance, tracking inventory, or optimizing energy usage. The next step is to select and deploy IoT devices that can seamlessly integrate with existing systems. It’s important to establish a reliable network infrastructure to ensure these devices can communicate effectively.
Once in place, the focus should be on data collection and analysis, enabling real-time monitoring and proactive maintenance. Pilot projects can be useful to test and refine IoT applications before full-scale deployment.
Key Actions
Data is the new currency in Industry 4.0, and leveraging it effectively is crucial for informed decision-making. To make the most of data, manufacturers should first establish a centralized data platform where information from IoT devices and other sources is aggregated. Advanced analytics tools can then be applied to this data to uncover actionable insights.
For instance, predictive analytics can forecast demand, optimize production schedules, and reduce waste. It’s also essential to train teams on data literacy to ensure they can interpret and act on insights effectively. Regular reviews of data-driven decisions help refine strategies and improve outcomes over time.
Key Actions
Automation is a cornerstone of Industry 4.0, enabling manufacturers to increase efficiency, reduce errors, and scale operations. To begin automating processes, companies should identify repetitive, time-consuming tasks that can benefit from automation. Robotics and AI-powered systems can be implemented to handle these tasks, allowing for greater precision and speed. Integrating automation with IoT devices ensures real-time data feeds into automated systems, further enhancing their effectiveness.
It’s crucial to start with small-scale automation projects to prove value and learn from the experience before scaling up. Additionally, continuous monitoring and optimization of automated processes are essential to maintain efficiency and adapt to changing needs.
Key Actions
As manufacturing systems become increasingly interconnected, ensuring cybersecurity and data privacy becomes paramount. The first step is to conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities across the digital landscape. Manufacturers should then implement multi-layered security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Regular updates and patches to software and hardware are critical to maintaining security over time. In addition, developing a robust incident response plan ensures that the organization is prepared to respond quickly and effectively in case of a breach. Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices and fostering a culture of vigilance is equally important in safeguarding the entire operation.
Key Actions
Overcoming resistance in manufacturing involves engaging workers early, demonstrating how new technologies will improve efficiency, and fostering a culture that supports innovation and digital adoption.
Provide targeted training programs to ensure that your manufacturing workforce is skilled in using advanced machinery and digital tools, crucial for maintaining productivity and competitiveness.
In manufacturing, prioritize investments in technologies that offer the highest return on investment while managing resources efficiently to support sustainable digital transformation.
Ensure new digital systems integrate smoothly with existing manufacturing equipment and processes, minimizing downtime and maximizing production efficiency across the facility.
Measuring the success of Industry 4.0 initiatives in the manufacturing sector requires a systematic approach to assess the impact of digital transformation efforts. Understanding the return on investment is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of implemented technologies and strategies.
To effectively measure success, organizations should establish Key Performance Indicators that align with their transformation goals. Common KPIs for Industry 4.0 include,
Operational Efficiency: Metrics such as production cycle time, machine uptime, and energy consumption can help gauge improvements in efficiency.
Product Quality: Defect rates, yield rates, and customer satisfaction levels provide insight into the quality enhancements achieved through automation and data-driven decision-making.
Cost Reduction: KPIs like cost per unit, inventory turnover, and waste reduction measure the financial impact of digital initiatives.
Employee Productivity: Labor efficiency, output per employee, and the impact of automation on workforce productivity are key indicators of success.
Time to Market: The time taken to develop and deliver new products is crucial for assessing the agility of the manufacturing process.
Once KPIs are established, continuous tracking is essential to ensure that the digital transformation initiatives are on the right path. Real-time data collection and analytics platforms play a significant role in monitoring performance. Dashboards can be used to visualize progress, making it easier for decision-makers to identify trends, areas of improvement, and any deviations from expected outcomes.
Regular reviews and reports should be scheduled to assess whether the transformation is achieving its intended objectives. By comparing actual performance against the set KPIs, organizations can determine the effectiveness of their strategies and make informed decisions on further steps.
Digital transformation is an ongoing process, and flexibility is key to its success. As the implementation progresses, feedback from the KPIs and other monitoring tools should be used to refine strategies. This could involve:
Revisiting Goals: If certain goals are not being met, it may be necessary to adjust them to better align with realistic outcomes or evolving business needs.
Optimizing Processes: Continuous improvement should be a focus, with regular tweaks to processes based on performance data.
Adapting to New Technologies: As technology evolves, the strategy may need to incorporate new tools and techniques to maintain competitiveness.
Resource Reallocation: Resources might need to be redistributed to areas showing the most potential for improvement or to address any unforeseen challenges.
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, adopting Industry 4.0 is no longer just an option; it’s a necessity for staying competitive. The integration of smart technologies into your operations can significantly boost efficiency, reduce costs, and open new avenues for growth. However, the journey toward digital transformation requires careful planning, strategic execution, and ongoing adaptation.
Partnering with experts who understand the unique challenges and opportunities of Industry 4.0 can make all the difference in ensuring a successful transformation. At Vrinsoft, we are committed to guiding manufacturers through every step of this process, from strategy development to technology implementation and beyond.
By taking decisive action now, you can position your business to thrive in the new era of manufacturing. Let Vrinsoft be your trusted partner in navigating this transformation, driving innovation, and achieving sustainable success. Reach out to us today to learn how we can help you harness the full potential of Industry 4.0.